Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Introduction
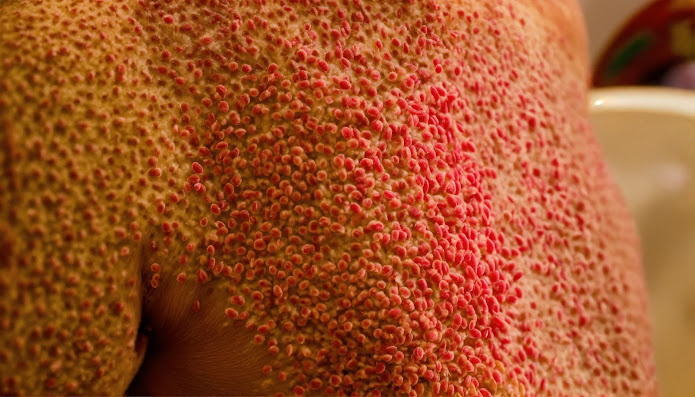
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a rare but serious disorder that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is typically triggered by a reaction to medication or, less commonly, an infection. SJS starts with flu-like symptoms, followed by a painful red or purplish rash that spreads and blisters, leading to the top layer of the skin to die and shed.
Symptoms
- Flu-like symptoms (fever, sore throat, fatigue)
- Painful red or purplish rash that spreads
- Blisters on the skin and mucous membranes
- Shedding of the skin
Causes
- Medications (antibiotics, anticonvulsants, NSAIDs)
- Infections (herpes, pneumonia)
Treatment
- Hospitalization: Patients are typically treated in a hospital, often in an intensive care unit or a burn center.
- Discontinuation of the Trigger: Immediate cessation of the suspected medication or treatment of the underlying infection.
- Supportive Care: Includes pain management, fluid replacement, wound care, and nutritional support.
- Medications: Sometimes corticosteroids or immunoglobulins are used, but their effectiveness is controversial.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Involves dermatologists, ophthalmologists, infectious disease specialists, and other healthcare professionals to manage various complications.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial to improving outcomes and preventing severe complications.


Comments
Post a Comment